Ailment Directory, Elixinol News, Parkinsons Disease, Total Body Wellness
A Holistic Approach to Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
The article outlines a six-part integrative medical approach to assist people with Parkinson’s disease (PD). According to some definitions PD is a chronic, incurable and progressively worsening disease with no known cause. However current research proposes that early stages of PD may be reversed or stabilized through an integrative medical approach which may also assist with side effects of pharmacological and surgical treatment plans.
Keywords: Parkinson’s Disease (PD), substantia nigra, striatum, dopamine, cellular health, mitochondria, therapeutic guidelines, fourth phase of water, medicinal cannabis, Integrative Medical Approach. Issued 1 October 2017.
A pdf download of this document is available here.
Contents
Symptoms of cellular health dysfunction at early and advanced stages of Idiopathic PD.
Symptoms of cellular health dysfunction at early and advanced stages of Familia PD.
Early Symptoms and Diagnosis of PD.
Pharmacological and Surgical Approach for Early Stages of PD.
Pharmacological and Surgical Approach for Advanced Stages of PD.
Therapeutic Guidelines for Non-Pharmacological Approach to PD.
Six Imbalances which can become Symptoms Labelled as PD.
Five measures for cellular health.
Tight Water Skin around the Mitochondria.
Integrative Medical Approach for the treatment of PD.
Use of Medicinal Cannabis in the Endocannabinoid Nerve System for PD.
Case Studies for Reversal and Stabilisation of PD.
Introduction
The aim of this article is to assist people with Parkinson’s disease (PD) to highlight research and treatment options which may assist in the reversal and stabilisation of PD. The article outlines the current definition of PD and links PD to cellular health. It also summarises the current therapeutic guidelines and side effects of pharmacological and surgical treatment plans. It then encourages an integrative medical approach, incorporating complimentary treatments such as emotional releases, cellular health and the use of medicinal cannabis.
Current Definition of PD
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke in Australia “PD is a chronic, incurable and progressively worsening neurological disorder” that results from degeneration of neurons in a region of the mid brain that controls movement (1). This degeneration creates a shortage of the brain signalling chemical (neurotransmitter) known as dopamine in the pathway between the Substantia Nigra and the Striatum, causing the movement impairment symptoms that characterise PD.
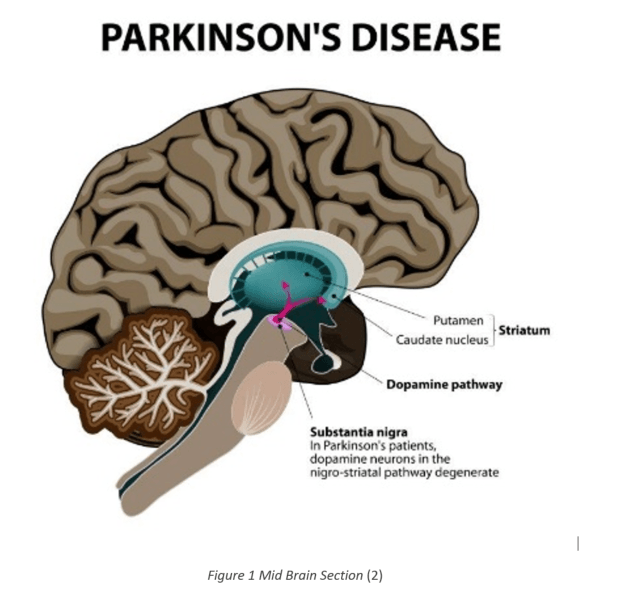
Figure 1 Mid Brain Section (2)
The cause of PD is unknown and there is presently no cure, the most common treatment options are medication and surgery which aim to manage the symptoms (3). Nearly one million people in the US (3) and over eighty thousand Australians were living with PD symptoms in 2016 (4).
A Deloitte Access Economics (DAE) article Living with PD describes PD as either Idiopathic or Familial (4). Idiopathic PD arises spontaneously, has no known cause and accounts for approximately 90% of PD diagnoses.
Symptoms of cellular health dysfunction at early and advanced stages of Idiopathic PD
Idiopathic PD cellular health can best be measured by Mitochondrial Dysfunction. The mitochondria convert nutrients and oxygen into the electrical supply of energy for the cell. The mitochondria are surrounded by the skin of water within the cell. The skin of the water or interfacial Exclusive Zone (EZ) Water is like a mesh (5). If the EZ water skin mesh is held tight from long term traumas then nutrients and oxygen supply to the mitochondria is reduced over time. If the EZ mesh is tight then the waste cannot be fully eliminated from the mitochondria. The Autophagy process of clearance of toxins and removal of dead nerve cells within the Substantia Nigra and the Striatum is inhibited (6).
Symptoms of cellular health dysfunction at early and advanced stages of Familia PD
Familial PD is genetically inherited and occurs when reduced cellular health activates Alpha-synuclein epigenetic mutations and or Methylation repression of the DNA within the mitochondria. (4). Other Familial PD cases now include mutations in the LRRK2, PARK7, PINK1, PRKN and SNCA genes (7).
Early Symptoms and Diagnosis of PD
The following are typical symptoms which present in PD patients. This list is not exhaustive of the initial symptoms, but these are indicators that could lead to a PD diagnosis.
- Muscle rigidity and pain- typically in the back or shoulder area, but not necessarily confined to those areas
- Loss of functionality in a hand- this is usually the loss of fine motor movement and control, for example doing up a shirt button becomes problematic
- Arm ceases to swing when walking
- Foot drags when walking- the patient may not be aware of this, but others may observe it
- Slowness of movement in the affected arm or leg
- Handwriting becomes awkward and shrinks
- Shaking in a limb – a tremor typically indicates Parkinson’s, however this may not be present at the early stage
(4) (8)
Therapeutic Guidelines
In Australia, Therapeutic Guidelines Limited publish guidelines to assist medical practitioners in the treatment of various diseases. The flowchart in the figure below outlines the symptoms and treatment options for early stages and advanced stages of PD.
Pharmacological and Surgical Approach for Early Stages of PD
The Therapeutic Guidelines recommend a pharmacological approach to treat severe tremors in the early stages of PD, as outlined in the figure below. This pharmacological approach includes dopamine replacement therapy such as dopamine agnostics, levodopa or amantadine. However, dopamine replacement therapy in the form of levodopa drugs cannot cross the blood brain barrier according to a number of medical professionals including UK Professor Matthew Wood (9) and USA doctors Dr. Kwang-Soo Kim (10) and Dr. Stanley Fahn (11). Carbidopa drugs are combined with levodopa drugs to replicate the dopamine transference in the pathway between the substantia nigra and the striatum.
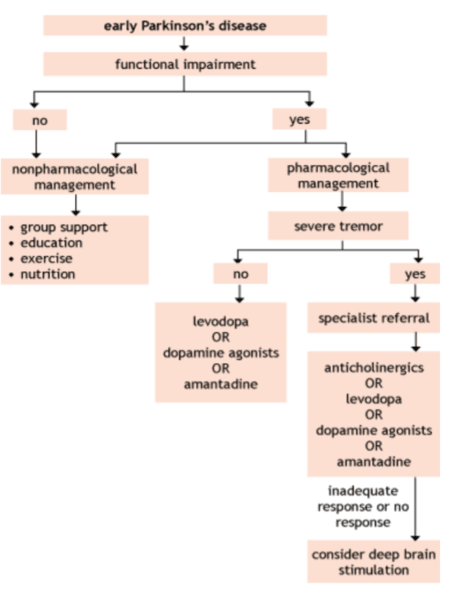
Figure 2 Early Parkinson’s Disease (12)
The current pharmacological treatment plan does not address the original cause/stressors which cause poor cellular health (13) which in turn reduces the function of the nerve cell mitochondria in the substantia nigra to produce dopamine. Research has recorded mitochondrial dysfunction for many PD patients (14) that results from cellular imbalances. Mitochondria produce energy within cells.
Parkinson’s Australia (15) list the iatrogenic side effects (inadvertently caused by medical treatment and pharmacological combinations) (16) from the the pharmacological treatment plan for early PD as, nausea, vomiting, constipation, postural hypotension, increased dreams and hallucinations. Levodopa induced dyskinesia has been found to effect 30-35% of patients just after twenty-four months of levodopa exposure (17).
Pharmacological and Surgical Approach for Advanced Stages of PD
During the advancing stages of PD the iatrogenic side effects of medication worsen and a wide range of debilitating non motor manifestations may occur. These are addressed by the medical profession with further medications prescribed. In addition, the dopamine replacement therapy treatments may wear off which worsens dyskinesia symptoms and deep brain stimulation surgery may be advised.
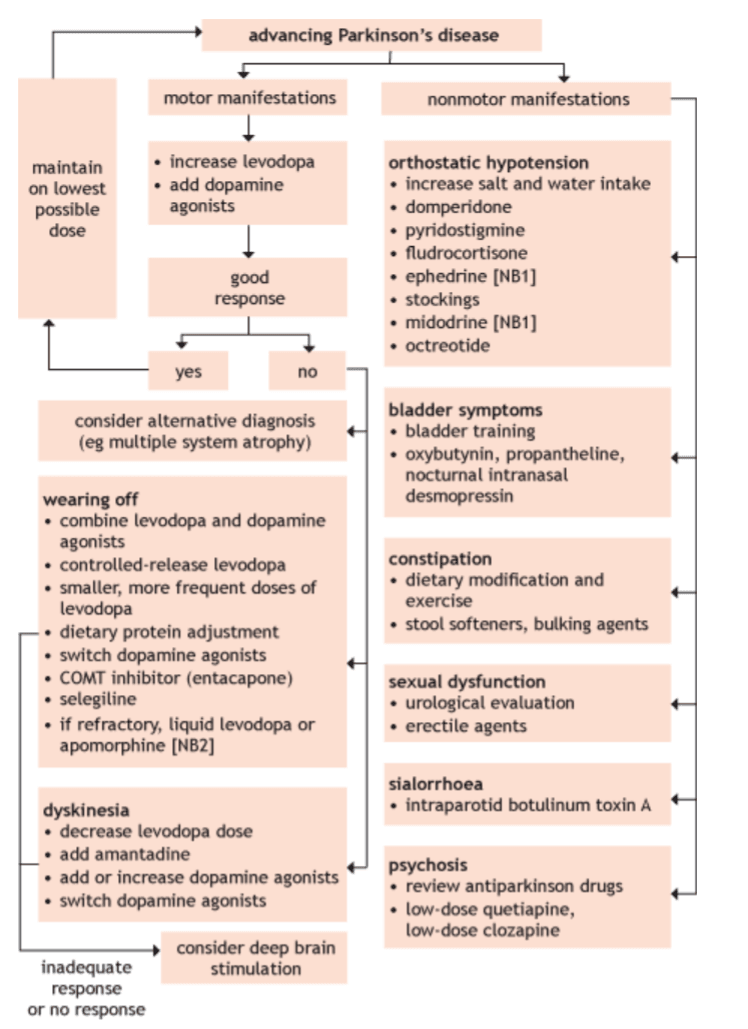
Figure 3 Advanced Parkinson’s Disease (12)
Therapeutic Guidelines for Non-Pharmacological Approach to PD
The Therapeutic Guidelines in Australia for non-pharmacological management of PD covers only four items; group discussion, education, exercise and nutrition. Expansion of these four items is included in the section on integrative medical approach to PD.
Six Imbalances which can become Symptoms Labelled as PD
In 2008 Dr Bradley Nelson issued the Body Code System of Natural Healing (18). He listed the 6 imbalances which cause symptoms that end up labelled as PD and other neurodegenerative disorders. The six imbalances are trapped emotions, infections/infestations, structural misalignment, nutritional deficiencies, toxins/poisons and energy field imbalances.
Short term stressors weaken the body and open the door for imbalances at a cellular level. Long term unresolved stressors compress the connective tissue in the myofascia (muscle skin) tissue, organs, cells, water skin within the cells, mitochondria dysfunction and can then lead to DNA mutations in a PD patient.
Five measures for cellular health
The table below outlines five measures of cellular health as summarized by Dr. Jerry Tennant (13). This is particularly relevant for PD patients who have low pH levels which causes chronic pain in addition to their other symptoms. Low oxygen levels in the cell reduces the function of the mitochondria. If these requirements for cellular health can be addressed then the symptoms of PD can in turn be addressed.
Table 1 Cellular Health Requirements (13)
| Requirements | Range for Cell | Abnormally High | Abnormally Low |
| Glucose | 80-110 mg/dl | Diabetes | Hypoglycemia |
| Temperature | 98.6° – 100° F 37° C | Fever | Hypothyroidism |
| Blood Pressure | 120-140/80-90 | Hypertension | Hypotension Dizziness |
| pH potential hydrogen | 7.35 – 7.45 | Throbbing pain | Chronic Pain as in PD |
| Oxygen | Pa02 > 95% | Doesn’t Occur | Anaerobic Metabolism > lactic Acid > lowered pH. As in severe PD tremoring |
Tight Water Skin around the Mitochondria
Dr. Gerry Pollack in The Fourth Phase of Water (5) showed the first three phases of water, as liquid, solid (ice) and gas (steam). Pollack outlines the fourth phase of water as the surrounding skin of bulk liquid water (H2O). This skin mesh is the liquid crystal Interfacial Exclusive Zone (EZ) H3O2. EZ water is negatively charged and is a hexagonal honeycomb-shaped mesh. At a cellular level the EZ holds bulk water within the cell and allows the transference of oxygen, nutrients and toxins through the mesh to various part of the cells including the mitochondria.
In a long term stressed situation, as experienced by PD patients, the EZ zone becomes a hardened Crystallised EZ mesh restricting the transference of oxygen, nutrients and toxins. As the toxins build in the Mitochondria this leads to reduced autophagy and epigenetic mutations.
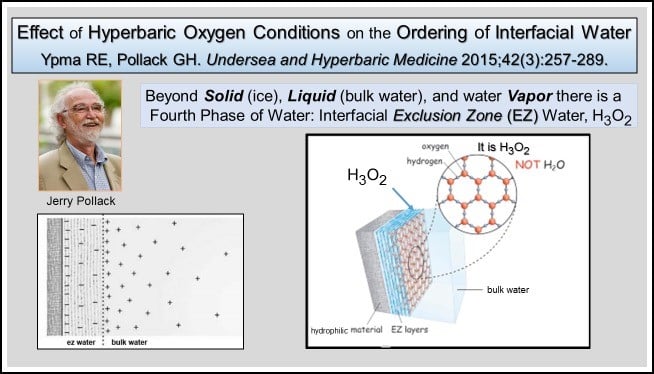
Figure 4 Interfacial Exclusive Zone (EZ) of Water (5)
Contrary to the current definition of PD, cellular health could be attributed as a cause of the disease. Poor cellular health leads to reduced energy production in the mitochondria. With reduced energy production the Substantia Nigra dopamine production is also reduced, as well as the Striatum’s ability to receive and use the dopamine required for normal movement.
Integrative Medical Approach for the treatment of PD
Integrative Medical Approach for the treatment of PD includes doctors, allied health, complementary and alternative therapies. The Holistic Health Model applies three levels of consciousness within the six aspects of the human body existing a unified field of torus energy (19) (20) (21) (20) (22) (23) (24).
![]()
Figure 5 Holistic Health Model includes six aspects of the Human Body (25)
Table 2 Integrative Medial Approach for the treatment of PD.
| Human Aspects (refer to Figure 5) |
Bodily Functions (refer to Figure 6) |
Conscious Levels (refer to Figure 7) |
Practitioners / Treatments |
| Physical Body | Structural systems of bones, muscles and connective tissue. | Subconscious mind autonomic systems. Where symptoms are identified as diseases. | Doctors, Allied Health, Chiro, Diet, Exercise, Naturopath, Physio, Remedial Massage, Yoga. |
| Emotional Body | Head to heart and gut integration. | Reactions between conscious mind and the heart and gut subconscious mind. | The Emotion Code (18), Byron Katie, EFT, NET, Myofascial Release, Neurolinking, PSYCH-K. |
| Mental Body | Brain in the head and Endocannabiniod Nerve System throughout the body for conduction of nerve instructions. | Conscious head brain, ego mind | Psychiatrists, Psychologists, Hypnotherapy, Mindfulness, Medicinal Cannabis, Essential oils. |
| Spiritual Body | Endocrine gland system, seven major chakras and fourteen Chinese meridian paths ways. | Subconscious mind, inner torus energy, chakra, prana, chi, energy. | Hands on therapies. Acupuncture, Reflexology Emmett, Ayurvedic Yoga, Auriculotherapy. |
| Energetic Body | Outer Torus Energy bubble or personal space. Heart to heart connection and cohesion. | Subconscious mind, heart to heart, environment and superconscious mind connection | Hands off Energetic and Vibrational therapies. Homeopathy, reiki, pranic, sound, art and colour therapies. |
| Eternal Body | Connection with others, the environment, life’s purpose and setting of vision and intentions. Fifth/Multi Dimension | Superconscious mind, heart connects with the universal mind and beyond time, space, infinity. | Meditation, Prayer, Past Life Akashic Records, Life Between Life Regressions, Near Death Experiences. Dreaming. |
Practitioners outlined in the table above can be accessed via (26). Complementary Therapies are listed and explained on the PD UK (27)and PD Australian (28) websites.

Figure 6 Unified Field of Torus Energy within and around the Human Body (29)
Dr. Bruce Lipton in his book The Biology of Belief (20) described the connection between the Conscious, Subconscious and Superconscious Mind within the Unified Field of Torus Energy. Three Minds of Consciousness explains the connect between every causal belief with every symptomatic effect used for diagnosis of a disease within the human body particularly for PD patients.

Figure 7 Conscious, Subconscious and Superconscious Mind within the Unified Field of Torus Energy (29)
Use of Medicinal Cannabis in the Endocannabinoid Nerve System for PD
Unlike traditional medications for PD, medicinal cannabis crosses the blood brain barrier to assist cellular health in the mid brain and in the endocannabinoid nerve system throughout the whole body. Forty years of global research has shown that Medicinal Cannabis with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Industrial Hemp cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to aid the repair the cannabinoid receptors markers in the synapsis region of the nerve cells to enable the transference of dopamine and other motor neuron instructions. (17) (30) (31) (32) (33).
Hemp comes in three product ranges.
- Dietary Supplements – industrial hemp seed products with nil cannabinoids can now be consumed in Australia in the form of seed, seed oil (high in omega oils 3, 6 and 9) and seed protein. Already available in health food stores and chemists.
- Industrial hemp CBD flower oil – with nil THC which is high in Cannabidiol (Hemp CBD oil) and low in tetrahydrocannabinol (THC psychoactive) is a natural raw cold pressed oil sold in the USA and Europe as a dietary supplement like olive oil. Useful for the health of the endocannabinoid nerve system. It is a preventative medical herb and useful as an antidepressant, counterbalance for those who are medicine sensitives and are suffering from the iatrogenic side effects of the PD pharmacological drug regime. Hemp CBD oil is classified by the TGA as a Schedule 4 Drug prescribable by an authorised GP or Specialist for an approved therapeutic purpose.
- Medicinal Cannabis flower products – with THC from the many varieties of cannabis/marijuana hemp plants. Medicinal Cannabis or Medical Marijuana flowers are heat processed to convert the THCa (THC acid) into the Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC psychoactive). Hemp Medicinal Cannabis is classified by the TGA as a Schedule 8 Drug prescribable by an authorised PD Neurologist for an approved therapeutic purpose. Research has been found Medicinal Cannabis to be useful to reduce the tremors or dyskinesia for PD patients.
The figure below outlines how hemp improves the Endocannabinoid Nerve System for PD patients.
Please note there are many other natural essential oils, supplements, nutrients, vitamins, herbal teas and antioxidants that cross the blood brain barrier and build cellular health. Many of these have these have been covered in the case study research in the next section.
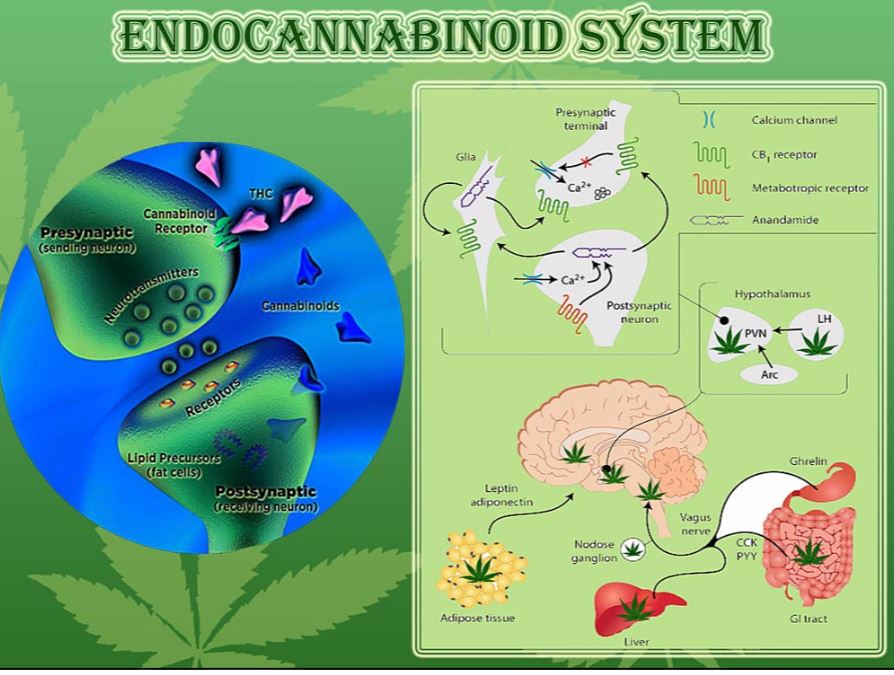
Figure 8 Endocannabinoid Nerve System and the effects on the Vagus Nerve (34)
Case Studies for Reversal and Stabilisation of PD
Examples of notable global reversal and stabilizations of PD may encourage patients and practitioners to apply an integrative medical approach to PD. These examples provide the patient and practitioner an opportunity to set a new direction and intentions for their expected PD outcomes.
Examples of reversals and stabilizations of PD.
- PD reversal through diet, nutrients and change of attitude. USA. Doctor John Gray. How I Reversed My PD Symptoms (35) This also includes the research of Dr. Marty Hinz (36) amino acid management of PD. (37) (38).
- 10 Step Naturopathic Parkinson’s Recovery Plan. Australia. John Coleman Naturopath from Melbourne. (39)
- Chiropractic Cellular Health and Medicinal Cannabis Parkinson’s Reversal Plan.USA. Dr. John Bergman Chiropractor. (37) Solutions for PD.
- Reversal of Parkinson’s with walking and Feldenkrais practitioners. South Africa. John Pepper (40). He is featured in The Brains Way of Healing by Dr. Norman Doidge (41).
- 20 step plan and reversal of side effects. Collin Potter (8)of Fighting Parkinson’s in the UK.
- Medicinal Cannabis to stabilize PD tremoring and dyskinesia USA. Larry Smith, movie “Riding with Larry” (42)
- Emotional release for PD patients. Australia. E-Motion Movie produced in Brisbane by Frazer Bailey and Justin Lyons (43). Emotion (energy in motion) experts from around the world share their wisdom and negative emotion clearing techniques to light a new pathway for humanity shows how to reverse unresolved trauma and stressors stored in the Emotional Body as is often found in PD patients.
- The use of anti-malaria treatments, chloroquine and amodiaquine, could bind and activate a protein Nurr1 in the brain vital to fight PD.Belmont MA. USA. Dr. Kwang-Soo Kim. “The Beginning of the end of PD” (10).
- Vitamins, supplements, teas and other drugs including Medicinal Cannabis for PD. Mexico City, Mexico. Dr. Ruben Martinez-Hernandez. ABC (American British Cowdray) Medical Centre. Movement Disorders, National Neurology Institute. (44)
- The Grain Brain Whole Life Plan, for brain vitality in PD. Miami, Florida USA. Dr. David Perlmutter, Neurologist. University of Miami, Millar School of Medicine. (45).
Conclusion
Parkinson’s disease should no longer be treated as an incurable, chronic disease with no cause. This article outlines cellular health as a potential cause of the disease. It also has highlighted the need for an integrated medical approach to release emotional traumas and improve cellular health. Medicinal cannabis proposed as a dietary supplement, to assist nerve cell function and reduction of dyskinesia in PD patients. A range of case studies where PD has been reversed or stabilised was outlined for patients and practitioners to further investigate.
References List
- (NINDS), National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Strokes. Parkinson’s Disease Information Sheet. s.l. : www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All-Disorders/Parkinsons-Disease-Information-Page, 2014.
- Fox, Michael J. What is Parkinson’s Disease. s.l. : http://shakeitup.org.au/understanding-parkinsons/, 2016.
- USA, Parkinsn’s Disease Foundation. What is Parkinson’s disease. New York : www.pdf.org/about_pd, 2013.
- Economics, Deloitte Access. Living with Parkinson’s Disease. An Updated Economic Analysis 2014. s.l. : Parkinson’s Australia Inc. and www.shakeitup.org.au/understanding-parkinsons/, August 2015.
- Pollack, Dr Professor Gerald. The Fourth Phase of Water: Beyond Solid Liquid and Vapor. Seattle : Ebner & Sons. http://faculty.washington.edu/ghp/, 2013.
- George F.G. Allen, Rachel Toth, John James & IanG.Ganley. Loss of iron triggers PINK1/Parkin-independent Mitophagy. s.l. : MRC-Protein Phosphorylation and Ubiquitylation Unit and Cell Signaling and Immunology, College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee, Dundee, UK EMBO reports (2013) 14, 1127–1135. doi, 2013.
- Reference, Genetics Home. Parkinson’s Disease. Inheritance and Familial PD. s.l. : https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/parkinson-disease#inheritance, 2017.
- Potter, Colin. Parkinson’s Recovery plan. Hants UK : https://www.fight-parkinsons.org/parkinsons-recovery/recovery-plan/, 2011.
- Wood, Dr Professor Matthew. A cure for Parkinson’s: Overcoming the blood brain barrier. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FxyXZD_I1qY&t=298s : Oxford University, for Parkinson’s UK.
- Kim, Dr Kwang-Soo. The Beginning of the End of Parkinson’s Disease. Belmont, MA . USA : www.dynamispictures.com/documentary-the-beginning-of-the-end-of-parkinsons-disease/ and http://www.mcleanhospital.org/news/2015/07/22/team-led-mclean-hospital-researcher-uncovers-potential-parkinsons-treatment, 2015.
- Fahn, Dr Stanley. Myths and Mistakes made by patients and doctors in PD Treatments. . Gainesville, Florida USA : Columbia University, University of Florida Centre for Movement Disorders and Neurorestoration and www.youtube.com/watch?v=utVZaOLUiDo 14th UF PD Symposium., 2016.
- Limited, Thereauputic Guideline. Thereauputic Guideline for Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease . s.l. : www.tg.org.au, 2007.
- Tennant, Dr. Jerry. Healing is Voltage. Colleyville, Texas USA : www.tennantinstitute.us, 2013 Third Edition.
- Nakamura, Dr. Ken. Alpha-Synucein and Mitochondria: Partners in Crime? UCSF San Francisco : Neurotherapeutics. 2013 Jul; 10(3):391-9. PMID: 23512373; PMCID: PMC3701775., 20 March 2013.
- Australia, Parkinson’s. Medical Options for Parkinson’s disease. Canberra : www.parkinsons.org.au/information_sheets , 2017.
- Webster, Merriam. Merriam-Webster Medical Dictionary. s.l. : Merriam-Webster and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iatrogenesis, Revised 15 February 2017.
- Choi, Sandeep Vasant More and Dong-Kug. Promising cannabinoid-based therapies for Parkinson’s disease: motor symptoms to neuroprotection. Department of Biotechnology, College of Biomedical and Health Science, Konkuk University, Chungju 380-701, South Korea : Molecular Neurodegeneration (2015) 10:17 DOI 10.1186/s13024-015-0012-0 BioMed Central and www.theroc.us/research-library, 2015.
- Nelson, Dr Bradley. Dr Bradley Nelson’s Body Code System of Natural Healing. New York USA : Wellness Unmasked Inc, 2008.
- Einstein, Albert. Photoelectric-Effect. Everything is Energy. s.l. : www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/quantum-physics/photons/a/photoelectric-effect, 1905.
- Lipton, Dr Bruce. Biology of Belief. s.l. : Hay House and www.brucelipton.com/store/the-biology-of-belief, 2005.
- Bohm, David. Quantum Theory. s.l. : http://dbohm.com/david-bohm-books.html#undivided and www.cosmometry.net/the-torus—dynamic-flow-process , 1951.
- Young, Arthur M. Mathematics, Physics and Reality. s.l. : Anodos Foundation and www.arthuryoung.com/aybooks.html, 1952.
- Gamble, Foster. Torus Energy in the Unified Field of Consciousness. USA : www.thrivemovement.com/the_movie, 2012.
- Emoto, Dr. Masaru. The Healing Power of Water. s.l. : Hay House, 2004.
- Vicary, Robert. Holistic Health Model of six aspects of the Human Body. Brisbane : www.alivetherapies.com.au/holistic-health-care/, 2016.
- —. Pratitioner Explanations Resources Links . Brisbane, Australia : www.alivetherapies.com.au/links/, 2017.
- UK, Parkinson’s. Complimentary Therapies and Parkinson’s. London UK : www.parkinsons.org.uk/information-and-support/complementary-therapies, 2017.
- Australia, Parkinson’s. Complmentary Therapies and Parkinson’s. Canberra Australia : www.parkinsons.org.au/symptom-management#complementary, 2017.
- Vicary, Robert. Head to Heart Integration and Coherence 2016. Brisbane : www.alivetherapies.com.au/head-to-heart-integration-and-coherence/ & www.heartmath.org.
- Caring, Realm of. Medicinal Cannabis and Hemp CBD (Cannabadiol) in the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. s.l. : www.theroc.us/research-library, 2000.
- Compassion, United in. UIC Medicinal Cannabis Course in Australia for Medical Practioners. Australia : www.unitedincompassion.com.au/Medical-Practitioners, 2017.
- Flower, Learn Green. Medicinal Cannabis Global Research. USA : www.learngreenflower.com/, 2017.
- Kapalos, Helen. A Life of its Own: The Truth about Medical Marijuana. 2017. Sydney Australia : www.sbs.com.au/guide/article/2017/04/03/comment-legal-use-medical-marijuana-human-right.
- Relief, Green. Endocannabinoid Nerve System and effects on the Vagus Nerve. Orange County CA USA : https://ocgreenrelief.org/alzheimers/endocannabinoid-system, 2016.
- Gray, Dr. John. How I Reversed my Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms. USA : www.marsvenus.com/blog/john-gray/how-i-reversed-my-parkinsons-disease-symptoms, 2012.
- Dr Marty Hinz, Dr Alvin Stein and Dr Thomas Uncini. Amino Acid Management of Parkinson’s Disease. . USA : www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3068871/, Int J Gen Med. 2011; 4: 165–174. Published online 2011 Feb 28. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S16621.
- Bergman, Dr John. Chiropractic Cellular Health and Medicinal Cannabis Parkinson’s Reversal Plan. Huntington Beach CA USA : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1_DBnv3Sa1k and https://drjohnbergman.com/, 2017.
- Nicolson, Garth L. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Chronic Disease: Treatment With Natural Supplements. USA : www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4566449/, Integr Med (Encinitas). 2014 Aug; 13(4): 35–43.
- Coleman, John. Naturopathic Parkinson’s Recovery Plan. Melbourne and Lancefield, Australia : www.parkinsonsrecoveryprogram.com and www.returntostillness.com.au, 1996.
- Pepper, John. Reverse Parkinson’s Disease with a Five Step Walking Plan. South Africa : www.reverseparkinsons.net/, 1992.
- Doidge, Dr Norman. The Brain’s Way of Healing. USA : www.normandoidge.com/, 2016.
- Smith, Larry. Medical Marijuana and Parkinson’s Part 3 of 3 and Riding with Larry Movie Ex Police Officer. USA : www.youtube.com/watch?v=zNT8Zo_sfwo and http://ridewithlarrymovie.com/.
- Lyons, Fraxer Bailey and Justin. E-Motion Movie. Brisbane, Australia : www.e-motionthemovie.com/, 2014.
- Martinez-Hernandez, Dr. Ruben. Vitamins, supplements, & other drugs including Medicinal Cannabis for Parkinson’s Disease. Gainesville, Florida, USA : Dr. Ruben Martinez-Hernandez. ABC (American British Cowdray) Medical Centre. Movement Disorders. National Neurology Institute. www.youtube.com/watch?v=M9UEihoEaDo UF 2017 PD Symposium, 2017.
- Dr. David Perlmutter. The Grain Brain Whole Life Plan for brain vitality in PD. Miami, Florida : University of Miami, Millar School of Medicine., 2016.



























Leave a reply